How to calculate monthly payments for loans in 2025? This is a crucial question as we navigate a complex financial landscape filled with various loan types and fluctuating interest rates. Understanding this process is essential for anyone looking to manage their finances effectively, whether for a home, car, or personal loan.
In 2025, the loan market will present diverse options, each impacting monthly payments differently. By breaking down the components of loan payments, exploring the amortization process, utilizing financial formulas, and considering online tools, we aim to empower borrowers with the knowledge to make informed decisions.
Understanding Loan Types
In 2025, individuals seeking financial assistance have a variety of loan types to choose from, each catering to different needs and circumstances. Understanding these loan types is crucial for prospective borrowers as it directly influences monthly payment calculations and overall financial planning.There are mainly four categories of loans available in 2025: personal loans, mortgage loans, auto loans, and student loans.
Each type comes with unique terms, interest rates, and payment structures, making it essential for borrowers to grasp how these factors will affect their monthly obligations.
Personal Loans
Personal loans are unsecured loans that can be used for various purposes, such as consolidating debt, financing a large purchase, or covering unexpected expenses. Generally, these loans have fixed interest rates and terms ranging from one to five years. The monthly payment calculation for personal loans is straightforward:
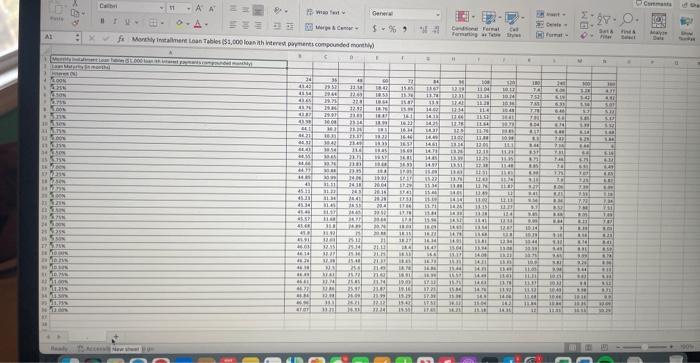
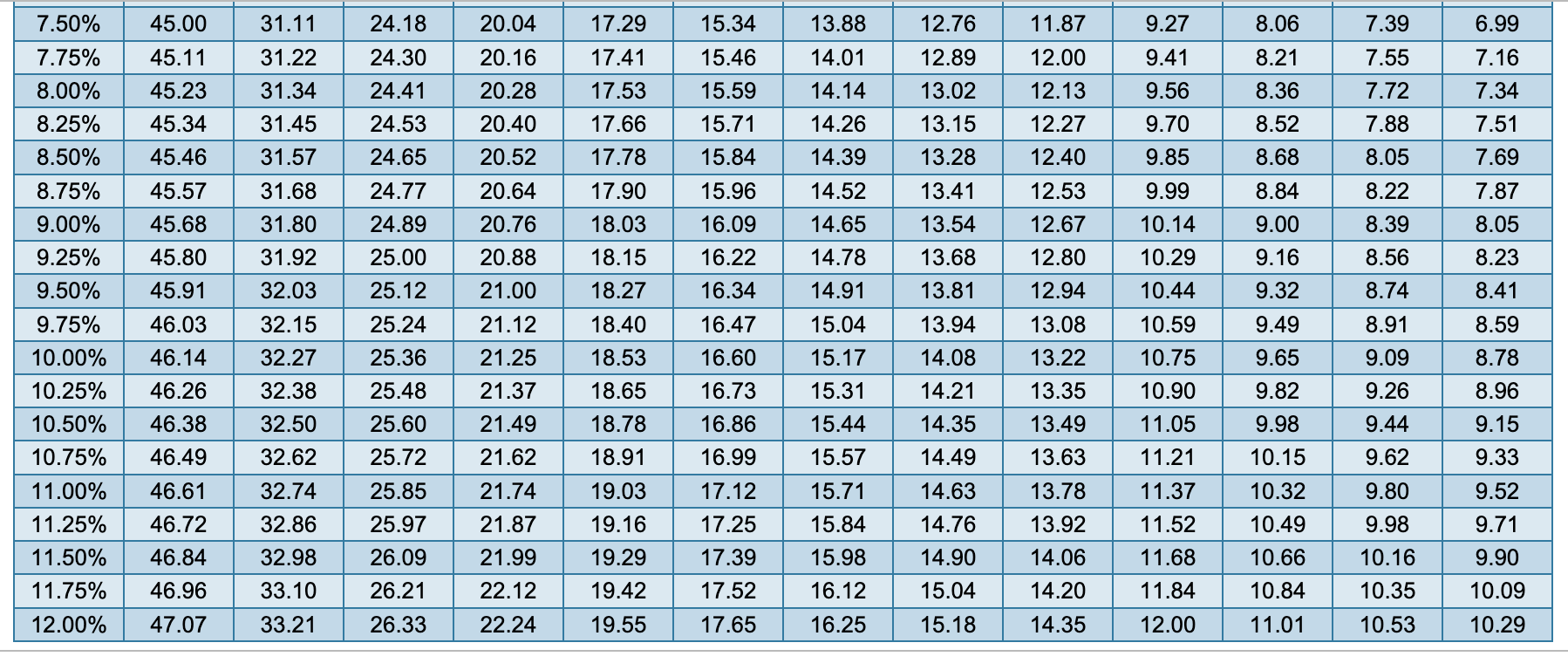
Monthly Payment = Loan Amount × (Monthly Interest Rate) / (1 – (1 + Monthly Interest Rate)^-Number of Payments)
The interest rates for personal loans can vary significantly based on the borrower’s credit score. For instance, a borrower with a high credit score may secure a rate as low as 5%, while those with lower scores may face rates up to 36%.
Mortgage Loans
Mortgage loans are specifically designed for purchasing real estate and typically come in fixed-rate and adjustable-rate (ARM) options. Fixed-rate mortgages maintain the same interest rate throughout the loan term, whereas ARMs have interest rates that can fluctuate based on market conditions.Monthly payments for mortgages are calculated similarly:
Monthly Payment = (Principal × Monthly Interest Rate) / (1 – (1 + Monthly Interest Rate)^-Total Number of Payments)
In 2025, mortgage interest rates are influenced by broader economic trends and can range between 3% to 7% depending on the lender and the borrower’s financial profile. A 1% increase in interest can significantly affect monthly payments, leading to higher overall costs over the life of the loan.
Auto Loans
Auto loans are secured loans specifically for purchasing vehicles, with the vehicle itself serving as collateral. These loans can have both fixed and variable interest rates. The loan terms typically range from three to seven years.Calculating monthly payments on an auto loan follows the same principle:
Monthly Payment = Loan Amount × (Monthly Interest Rate) / (1 – (1 + Monthly Interest Rate)^-Number of Payments)
Interest rates for auto loans can vary based on the age of the vehicle and the buyer’s creditworthiness. In 2025, borrowers might find rates from 4% to 10%, emphasizing the importance of shopping around for the best deal.
Student Loans
Student loans can be either federal or private. Federal loans often offer lower interest rates and more flexible repayment options, while private loans come with terms set by individual lenders. The monthly payments for student loans are calculated similarly to personal loans but may include options for income-driven repayment plans. In 2025, federal student loan interest rates are projected to be around 3% to 6%, depending on the type of loan (subsidized vs.
unsubsidized). Understanding these different loan types, their payment structures, and the potential interest rate implications helps borrowers make informed financial decisions in 2025, ultimately leading to better management of their monthly payment obligations.
Key Components of Loan Payments
Understanding the key components of loan payments is essential for borrowers as it allows them to evaluate their financial commitments effectively. Monthly loan payments are typically comprised of several factors, including principal, interest, taxes, and insurance. Each of these components plays a crucial role in determining the total amount you will pay each month.The principal is the original sum of money borrowed, while interest is the cost of borrowing that principal.
Taxes and insurance, often included in monthly payments, ensure that property taxes and necessary insurance premiums are accounted for, protecting both the lender and the borrower.
Detailed Breakdown of Loan Payment Components
When borrowing money, it is vital to understand how each component of the loan payment is calculated. Here’s a closer look at each element:
- Principal: This is the initial amount borrowed. For example, if you take out a mortgage for $200,000, that is your principal. Each monthly payment reduces this principal balance.
- Interest: This is the fee charged by the lender for borrowing money. Interest rates can be fixed or variable. If you have a fixed-rate mortgage at a 4% annual interest rate, your monthly interest is calculated on the remaining balance of the principal.
- Taxes: Property taxes vary by location and are typically assessed by local governments. These taxes can be estimated based on the property’s assessed value and the local tax rate. A house valued at $300,000 with a tax rate of 1% would incur annual taxes of $3,000, adding $250 to your monthly payment.
- Insurance: Homeowner’s insurance protects your property and is often required by lenders. The cost can vary significantly based on factors like coverage amount and location. For instance, if your annual insurance premium is $1,200, it adds another $100 per month to your total payment.
Example Calculation of Monthly Payments
To concretely illustrate how these components work together, consider an example loan scenario:
Loan Amount (Principal)
$250,000
Interest Rate
3.5% (fixed)
Property Taxes
$2,400 annually (or $200 monthly)
Insurance
$1,200 annually (or $100 monthly)Using the formula for monthly payments on a fixed-rate mortgage:
M = P [ r(1 + r)^n ] / [ (1 + r)^n – 1 ]
Where:
- M = total monthly mortgage payment
- P = loan principal ($250,000)
- r = monthly interest rate (annual rate / 12 months = 0.035 / 12)
- n = number of payments (loan term in months)
The monthly payment for the mortgage (principal and interest) can be calculated, then added to the monthly insurance and property tax for the total monthly payment.
Comparison of Loan Payment Components by Loan Type
Here’s a simplified comparison table that Artikels how these components can vary across different types of loans:
| Loan Type | Principal | Interest Rate | Taxes | Insurance |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Conventional Mortgage | $300,000 | 4.0% | $250/month | $120/month |
| FHA Loan | $250,000 | 3.5% | $200/month | $100/month |
| VA Loan | $350,000 | 3.25% | $300/month | $150/month |
| Auto Loan | $30,000 | 5.0% | N/A | N/A |
This table highlights how different loan types can impact the components of monthly payments, helping borrowers make informed decisions.
The Amortization Process: How To Calculate Monthly Payments For Loans In 2025?
Amortization is a fundamental concept in the realm of loans that provides borrowers with a clearer understanding of how their payments are allocated over time. It refers to the gradual repayment of a loan through regular payments that cover both principal and interest. This process is not only significant for borrowers in managing their debt but also for lenders in assessing the risk of repayment.The amortization schedule Artikels the payment plan for a loan, detailing how much of each payment goes toward the principal and how much goes toward interest.
This transparency helps borrowers see how their outstanding balance decreases over time, making it easier to track progress and plan finances.
Sample Amortization Schedule
Creating a sample amortization schedule can clarify how payments are structured. For instance, consider a hypothetical loan of $10,000 with a 5% annual interest rate, to be repaid over five years. Below is a simplified amortization schedule for this loan.
| Payment Number | Payment Amount | Interest Payment | Principal Payment | Remaining Balance |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | $188.71 | $41.67 | $147.04 | $9,852.96 |
| 2 | $188.71 | $41.05 | $147.66 | $9,705.30 |
| 3 | $188.71 | $40.45 | $148.26 | $9,557.04 |
| 4 | $188.71 | $39.65 | $149.06 | $9,407.98 |
| 5 | $188.71 | $39.03 | $149.68 | $9,258.30 |
This table continues until the loan is fully amortized after 60 months, highlighting how the interest component decreases while the principal payment increases over time.
Methods of Amortization
Different methods of amortization can affect monthly payments significantly. Understanding these methods allows borrowers to choose the one that best suits their financial situations.The three primary methods include:
- Fixed Amortization: This is the most common method where the monthly payment remains constant throughout the loan term. A larger portion of the early payments goes towards interest, with more going to the principal as the loan matures.
- Graduated Amortization: Payments start lower and gradually increase at predetermined intervals, which can be beneficial for borrowers expecting higher future income. This method can lead to significantly higher total interest costs over the life of the loan.
- Negative Amortization: This occurs when monthly payments are less than the interest due, leading to an increase in the principal balance over time. This method can be risky, as it may result in larger payments later on when the borrower is already financially strained.
Understanding these methods helps borrowers make informed decisions regarding their loan contracts.
“Amortization is the key to understanding how loan payments impact overall financial health.”
Using Financial Formulas
Calculating monthly loan payments is crucial for understanding overall loan costs and managing your budget effectively. By using a simple financial formula, you can determine exactly how much you need to pay each month, allowing you to plan accordingly.The formula for calculating monthly loan payments is derived from the concept of amortization, which involves spreading the loan amount over a certain period while accounting for interest.
The formula is as follows:
M = P [ r(1 + r)^n ] / [ (1 + r)^n – 1 ]
In this formula:
- M = Monthly payment
- P = Principal loan amount
- r = Monthly interest rate (annual rate divided by 12)
- n = Number of payments (loan term in months)
Applying the Formula with Real-World Examples
Understanding how to apply the formula effectively can make a huge difference in your financial planning. Here’s how to compute monthly payments using real-world examples.Let’s assume you take out a loan of $20,000 at an annual interest rate of 5% for a term of 5 years. First, convert the annual rate into a monthly rate and calculate the number of payments:
- Monthly interest rate (r) = 5% / 12 = 0.4167% = 0.004167
- Number of payments (n) = 5 years × 12 months/year = 60 months
Now plug these values into the formula:
M = 20000 [ 0.004167(1 + 0.004167)^60 ] / [ (1 + 0.004167)^60 – 1 ]
After performing the calculations, you would find that the monthly payment (M) is approximately $377.42.For another example, consider a $10,000 loan at an annual interest rate of 7% for 3 years.
- Monthly interest rate (r) = 7% / 12 = 0.5833% = 0.005833
- Number of payments (n) = 3 years × 12 months/year = 36 months
Using the formula:
M = 10000 [ 0.005833(1 + 0.005833)^36 ] / [ (1 + 0.005833)^36 – 1 ]
After calculating, the monthly payment (M) is approximately $322.67.
Step-by-Step Guide on Calculating Payments, How to calculate monthly payments for loans in 2025?
Calculating loan payments can be broken down into a series of manageable steps, making it easier for anyone to follow. Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to proceed:
1. Identify Loan Amount (P)
Determine how much money you wish to borrow.
2. Determine Interest Rate
Find out the annual interest rate from your lender.
3. Convert Interest Rate
Divide the annual interest rate by 12 to get the monthly rate.
4. Establish Loan Term (n)
Decide how many months you will be repaying the loan.
5. Apply the Formula
Insert your values into the monthly payment formula.
6. Calculate
Perform the mathematical operations to find your monthly payment.By following these steps, you can accurately compute your monthly payments for various loan amounts and interest rates, helping you manage your financial responsibilities more effectively.
Online Calculators and Tools
In the digital age, online calculators and tools have become essential for individuals looking to calculate their monthly loan payments. With the increasing number of options available in 2025, these tools simplify the loan payment process and offer quick results with minimal effort. Users can easily access these resources from their computers or smartphones, making them an attractive choice for tech-savvy borrowers.When utilizing online calculators, it’s important to understand their benefits and limitations.
While they provide convenience and immediate results, they can sometimes lack personalization and in-depth analysis. These tools typically calculate payments based on standard formulas, which may not account for specific factors unique to each borrower’s financial situation.
Popular Online Loan Calculators
Several online tools stand out in the crowded field of loan payment calculators. Below is a list of some of the most popular options available in 2025:
- Bankrate Loan Calculator
- Zillow Mortgage Calculator
- Calculator.net Loan Calculator
- MortgageCalculator.org
- SmartAsset Loan Calculator
These calculators offer various features that cater to different user needs. Below is a comparison of some key features among these popular loan calculators:
| Calculator | Amortization Schedule | Extra Payment Options | Mobile Accessibility | Customizable Terms |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bankrate Loan Calculator | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Zillow Mortgage Calculator | Yes | No | Yes | Yes |
| Calculator.net Loan Calculator | Yes | Yes | Yes | No |
| MortgageCalculator.org | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| SmartAsset Loan Calculator | No | Yes | Yes | Yes |
Each calculator has its unique strengths. For instance, the Bankrate Loan Calculator offers comprehensive features including an amortization schedule and extra payment options, making it versatile for various financial scenarios. In contrast, SmartAsset focuses on providing a streamlined experience but lacks an amortization schedule, which might be a critical feature for some users.
“The right loan calculator can save you time and help you make informed financial decisions, ensuring you understand your loan obligations thoroughly.”
Factors Influencing Loan Payments
Understanding the factors that can influence monthly loan payments is crucial for anyone looking to borrow money. These factors range from personal financial health to broader economic conditions. In 2025, various elements will come into play that can either increase or decrease the monthly obligation of a borrower.
External Factors Affecting Loan Payments
Several external conditions can significantly shape the amount you pay each month on a loan. Recognizing these factors can help borrowers make informed decisions. Here are some key influences:
- Interest Rates: The prevailing interest rates in the economy directly impact monthly payments. Higher rates lead to increased costs, while lower rates can make borrowing more affordable.
- Inflation: Rising inflation can affect purchasing power and, ultimately, the cost of borrowing. Lenders may adjust rates based on anticipated inflation to maintain profitability.
- Market Competition: The level of competition among lenders influences interest rates and loan products offered. More competition can lead to better rates and terms for borrowers.
- Regulatory Changes: New laws and regulations can modify lending practices and consumer protections, impacting how lenders calculate payments and fees.
Role of Credit Scores in Interest Rates and Payments
Credit scores play a pivotal role in determining the interest rates offered to borrowers. A higher credit score generally translates to lower interest rates, resulting in reduced monthly payments. Conversely, lower credit scores may lead to higher rates, increasing the financial burden.
“Good credit can save you thousands over the life of a loan.”
For instance, a borrower with a credit score above 740 might secure a mortgage rate of 3.5%, while someone with a score below 620 could face rates near 5.5%. This difference can lead to hundreds of dollars in additional payments each month.
Economic Trends in 2025 Affecting Loan Payments
As we look ahead to 2025, several economic trends could influence loan payment calculations. Awareness of these trends allows borrowers to prepare for potential changes in their financial landscape.
- Job Market Stability: A stable job market can boost consumer confidence, leading to increased lending and spending. Conversely, economic downturns can tighten credit availability and increase rates.
- Housing Market Fluctuations: Changes in home prices can affect mortgage payments. A booming housing market may lead to higher loan amounts and potential adjustments in interest rates.
- Technological Advancements: The rise of fintech companies offers more competitive rates and innovative loan products, potentially reshaping the lending landscape.
- Global Economic Events: Economic conditions in other countries can influence domestic interest rates and lending practices, as interconnected economies can lead to shared risks and benefits.
Budgeting for Loan Payments
Effectively budgeting for loan payments is essential for maintaining financial stability and avoiding debt traps. By understanding your monthly obligations and integrating them into your overall financial picture, you can ensure timely payments while still managing other living expenses.When budgeting for loan payments, it is crucial to take into account not only the loan amount but also your income and other financial obligations.
This comprehensive approach helps in creating a realistic budget that accommodates your monthly payments while allowing for savings and discretionary spending.
Strategies for Managing Loan Payments with Other Financial Obligations
Incorporating loan payments into your budget requires a strategic approach. Here are some effective strategies to help manage your finances:
- Track Your Income and Expenses: Begin by listing all sources of income and your fixed and variable expenses. This gives you a clear picture of your financial situation.
- Prioritize Loan Payments: Treat your loan payments as non-negotiable expenses. Allocate funds for them as soon as you receive your paycheck to avoid any risk of missing payments.
- Create a Contingency Fund: Setting aside a small amount each month for unexpected expenses can prevent you from falling behind on your loan payments if emergencies arise.
- Use the 50/30/20 Budgeting Rule: Allocate 50% of your income to needs (including loan payments), 30% to wants, and 20% to savings. This method helps balance loan repayments with other financial goals.
In addition to strategies, applying specific budgeting methods can significantly enhance your ability to manage loan repayments effectively.
Budgeting Methods Incorporating Loan Repayments
Employing systematic budgeting methods can simplify the process of managing loan payments. The following budgeting methods can be particularly beneficial:
- Envelope System: Allocate cash into envelopes designated for different spending categories. One envelope should be specifically for loan payments, ensuring that funds are set aside and protected from other expenditures.
- Zero-Based Budgeting: This method requires you to assign every dollar of your income to specific expenses, including loan payments. By doing this, you ensure that every dollar has a purpose, leaving no room for overspending.
- Digital Budgeting Tools: Utilize budgeting apps that allow you to track your income, expenses, and loan payments in real-time. Many apps offer reminders for upcoming payments and can help adjust your budget as necessary.
By employing these strategies and methods, you can effectively manage your loan payments alongside other financial obligations, keeping your finances on track and reducing stress related to debt management.
Refinancing Options
Refinancing can be a strategic financial decision, allowing borrowers to adjust their loan terms to better fit their current financial situation. This process involves replacing an existing loan with a new one, often to secure lower interest rates, reduce monthly payments, or change loan duration. Understanding the key aspects of refinancing can help you make informed choices that align with your financial goals.Refinancing involves several steps, including assessing your current loan, evaluating your credit score, and comparing offers from various lenders.
Typically, it’s beneficial to consider refinancing if interest rates have dropped since your original loan, or if your credit score has improved significantly, allowing you to qualify for better terms. Additionally, refinancing may allow you to consolidate multiple loans into one, simplifying your payment structure.
Comparison of Refinancing and Maintaining Current Loans
Opting to refinance a loan instead of maintaining the current loan can lead to significant financial implications. Here’s a breakdown of the major differences between the two options:
- Interest Rate: Refinancing often allows you to secure a lower interest rate, which can lead to substantial savings over time, compared to sticking with a higher-rate loan.
- Monthly Payments: A new loan with extended terms might decrease your monthly payments, making it more manageable compared to your current obligations.
- Loan Duration: Refinancing may change the length of your repayment period, allowing you to pay off the loan faster or extend it for lower payments.
- Fees and Costs: There are costs associated with refinancing, such as closing costs and application fees, which need to be weighed against potential savings.
- Loan Structure: Refinancing can provide an opportunity to switch from an adjustable-rate mortgage to a fixed-rate mortgage, offering more predictable payments.
The potential savings from refinancing can be illustrated with hypothetical scenarios. For instance, consider a homeowner with a $200,000 mortgage at a 5% interest rate. Their monthly payment might be around $1,073. If interest rates drop to 3.5%, refinancing could reduce that monthly payment to about $898, saving the homeowner over $175 each month. Over a typical 30-year term, that could amount to nearly $63,000 in savings on interest alone.Another scenario involves a borrower with multiple high-interest loans totaling $50,000 at an average interest rate of 8%.
If they refinance these loans into a single loan at 5%, they could lower their monthly payment and streamline their finances, saving both time and money.In summary, refinancing can provide numerous benefits, but it’s crucial to assess your financial situation, the current market rates, and the terms of your existing loans to ensure that it is the right choice for you.
FAQ Explained
What factors affect my monthly loan payment?
Factors include loan amount, interest rate, loan term, and additional costs like taxes and insurance.
Can I use online calculators for accuracy?
Yes, online calculators can provide a quick estimate, but always double-check with a financial advisor for precision.
Is it better to refinance my loan?
Refinancing can be beneficial if it lowers your interest rate or reduces your monthly payment, but consider the costs involved.
How does my credit score impact my loan payment?
A higher credit score typically results in lower interest rates, leading to lower monthly payments.
What is amortization and why is it important?
Amortization is the process of spreading out loan payments; understanding it helps you know how payments are applied to principal and interest over time.